Understanding Print-on-Demand Book Pricing

Print-on-Demand (POD) book printing is becoming increasingly popular as an economical alternative to traditional print runs. But when it comes to the pricing associated with POD printing, things may seem a bit unclear.
Let’s see a few things about print-on-demand and guidelines on how to price your print-on-demand book.
In this article, I go over:
- What Is Print-on-Demand?
- Benefits of Using Print-on-Demand as an Author
- Factors to Consider When Pricing Your Print-on-Demand Book
- Print-on-Demand Pricing Model
- Print-on-Demand Book Distribution
- Print-on-Demand Platform or an Aggregator?
- How to Publish Your Print-on-Demand Book with PublishDrive
- Pitch Your Book to Local Bookstores
What Is Print-on-Demand?
Print-on-demand (POD) is a type of publishing in which books are printed and shipped to customers as orders come in, rather than having to print a large number of books ahead of time.
POD eliminates the need to pay for expensive inventory upfront, as books are only printed once an order is placed.
Benefits of Using Print-on-Demand as an Author
Print-on-demand has a huge positive impact on the environment, eliminating waste and overproduction. But it’s also highly advantageous for the authors that opt for this service. Here are some of the benefits:
1. Quick and easy availability
With print-on-demand, authors can make their books quickly and easily available to readers without having to wait for a traditional publisher to accept their work.
2. No need for expensive inventory
Print-on-demand eliminates the need to pay for expensive inventory upfront, as books are only printed once an order is placed.
3. Lower production costs
Since print-on-demand allows for smaller print runs, it can result in lower production costs compared to traditional offset printing.
4. More control over the publishing process
With print-on-demand, authors have more control over the publishing process, including the design and layout of their books.
5. Improved profit margins
Authors only pay for the books that are actually sold rather than having to pay for a large print run upfront.
6. Books never run out of stock
The book is printed as soon as it’s ordered, which means it can’t run out of stock. All while never occupying space on the shelves.
Factors to Consider When Pricing Your Print-on-Demand Book
1. The cost of production, including the cost of paper, ink, and bookbinding materials
When it comes to the cost of production for print-on-demand books, you have to consider the type of printing used. Digital printing is the most common method for print-on-demand books, as it allows for smaller print runs and variable data printing.
The cost of digital printing is generally higher per unit than traditional offset printing, but it eliminates the need for large print runs, which can be costly.
The cost of bookbinding will also affect the production cost: hardcover books will typically be more expensive than paperback books.
Also, it's important to consider any additional expenses, such as proofreading and cover design, which can add to the overall cost of production.
2. The shipping costs
The shipping cost for print-on-demand books can vary depending on several factors, such as the destination country, package weight, book size, and shipping method. Different print-on-demand providers may have different pricing structures and shipping options.
To determine the specific shipping cost for print-on-demand books, you should check the print-on-demand service provider you are using. They usually have a shipping cost calculator (as we’ll see in a minute) or provide detailed information on their website regarding shipping rates for different regions.
Bear in mind that shipping costs can vary significantly between domestic and international shipments. International shipping, in particular, may be more expensive due to customs fees, import duties, and longer transit distances.
3. Distribution fees
If you choose to distribute your book through a POD service, they may take a percentage of your royalty as a distribution fee.
4. Market demand
The price of your book should reflect the market demand for similar books in your genre and category. Research the market value of similar books in your genre or category. Look at the prices of books that are similar in content, format, and target audience. This will give you an idea of what readers are willing to pay for books like yours.
5. Author reputation
If you are an established author with a large following, you can charge a higher price for your book. If you’re only starting out, set a lower price for your book, but not as low as to lose profit.
Print-on-Demand Pricing Model
One print-on-demand pricing model is to set a base price for your book that covers the cost of production and then add a markup to determine your profit margin.
The markup can be a percentage of the base price or a fixed amount per unit sold.
Here’s an example of a print-on-demand pricing strategy:
- set a base price for your book that covers the cost of production, such as $10 for a paperback book
- add a markup to determine your profit margin; let’s say 50% of the base price, making the final price for the book $15
- this gives you a $5 profit per unit sold
To be sure of the markup you should add, you can check your POD’s service calculator. More on this in a minute.
Print-on-Demand Book Distribution
You now have an idea about how to calculate the print production cost, but you should also know about book distribution. You can either search for a print-on-demand company or an aggregator to distribute to more places at once.
Let’s start with a list of print-on-demand companies.
1. IngramSpark
IngramSpark is one of the best print-on-demand publishers to know, reaching more than 39,000 online stores. These stores include major bookstores like Barnes & Noble as well as numerous libraries.
Royalties: 45-70%
As mentioned, you should add a markup to the book production price, and IngramSpark has a Print and Ship Calculator to help you with this.
Go to IngramSpark’s Print and Ship Calculator and add all the required information, such as trim size, interior color and paper, bookbinding, cover finish, and page count.
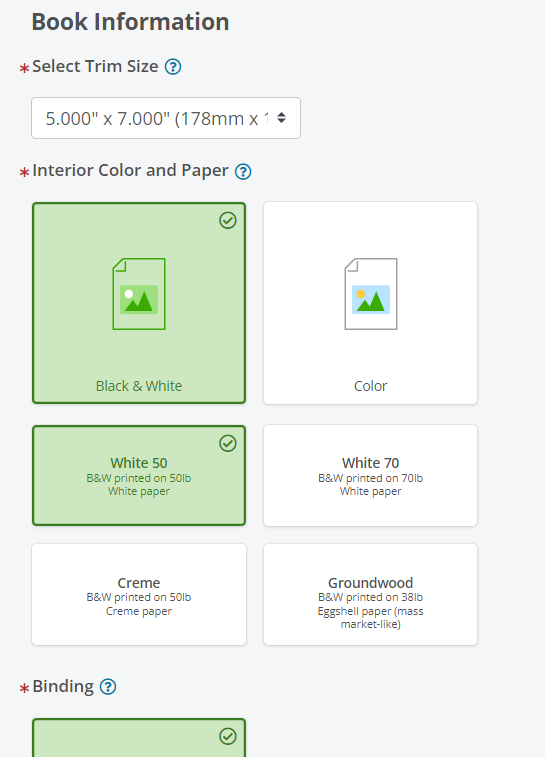
Then, add the shipping information:
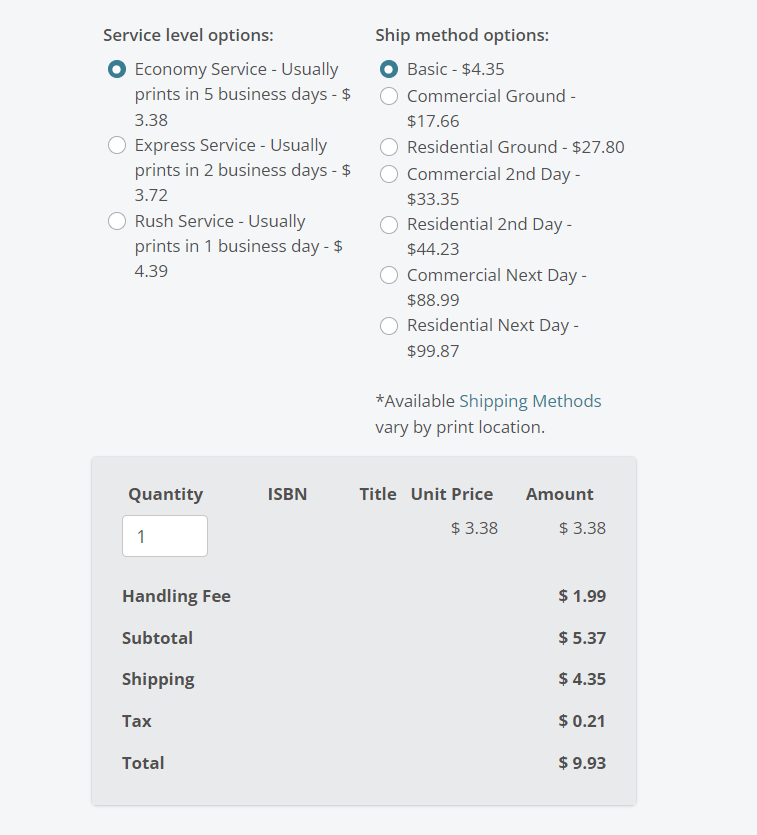
Once you’ve filled out all the information, calculate the print and shipping costs:
To this price, you can add your markup and have the final price.
2. KDP Print
Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) integrates print-on-demand with its brick-and-mortar stores in 13 countries. You can set up print-on-demand books on the KDP platform.
Royalties: 40-60%
Note: Amazon changed the print-on-demand costs for the first time since 2016. You should check here the new vs. old prices.
Amazon has a similar calculator to help you estimate your production costs and royalties:
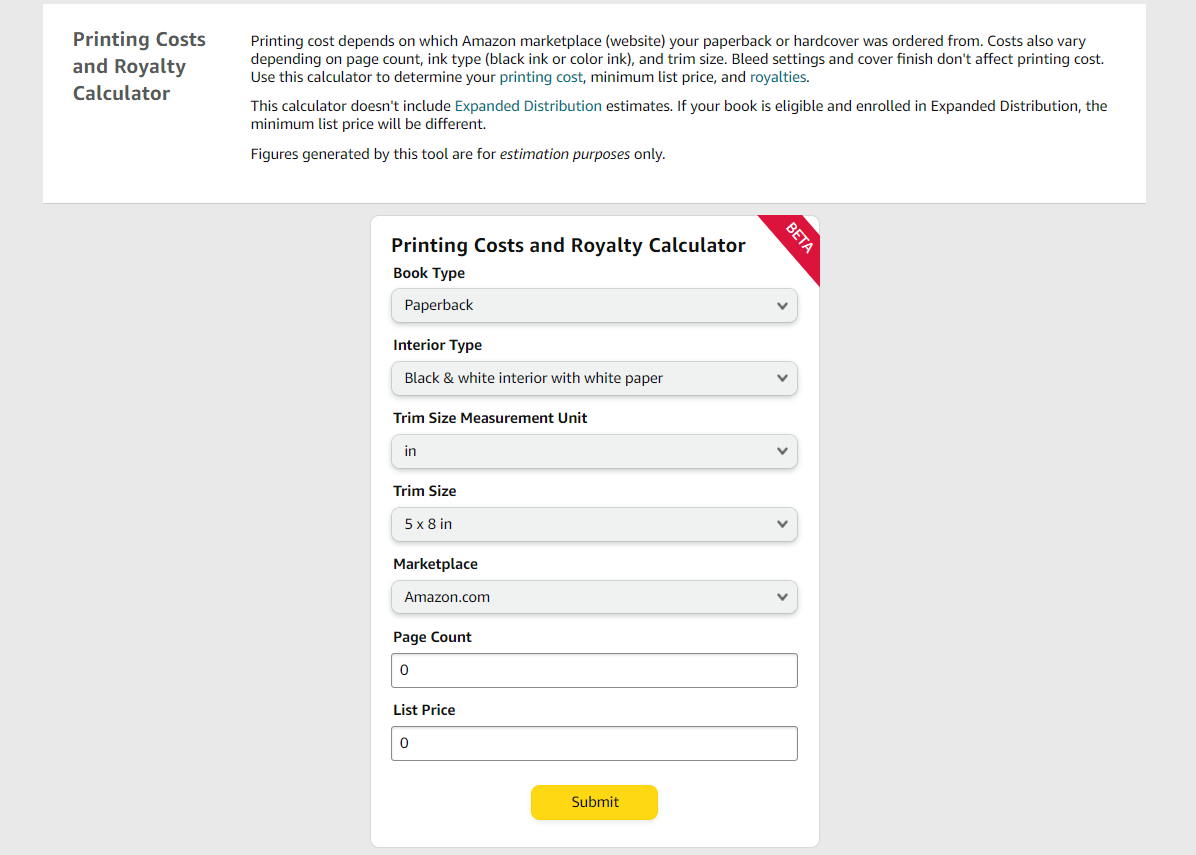
3. Blurb
Blurb provides a user-friendly platform for creating your print-on-demand book. However, it is more expensive compared to other options. Blurb stands out through its creation of photobooks, which is an excellent option for independent authors selling graphic novels or other books that have many visual elements.
After uploading and designing your book on the Blurb platform, the initial cost depends on the format you select, such as photo, paperback, or magazine. Then, you have the option to make your book available for purchase on Blurb's website or through other retailers facilitated by IngramSpark.
Royalties: 45-64%
4. Bookvault
Bookvault is a POD service platform that can help you sell directly on your website with various apps, plugins, and integrations. You also get the option to sell to their distribution networks like Amazon, IngramSpark, Gardners, and The Great British Book Shop.
Setup fee: $23
Royalties: 40-90%
5. BookBaby
BookBaby is the priciest option but great for indies looking for bulk orders. BookBaby’s distribution network includes all of IngramSpark’s stores, plus other retailers.
Setup fee: $399
Royalties: 45%
Print-on-Demand Platform or an Aggregator?
We've seen a list of the top POD distributors out there. You can choose one of those, or you can go to PublishDrive and distribute to IngramSpark and Amazon Print at the same time.
On top of that, PublishDrive helps you sell in markets like China through CNPeReading, where there are literally millions of readers wanting print books.
CNPeReading distributes to JD, a giant retailer capturing 30% of the Chinese market, and Dangdang, another prominent bookseller in China, with 30 million monthly visitors to its online store.
What is PublishDrive? An aggregator that helps indie authors and publishers publish, distribute and promote their ebooks, audiobooks, and print-on-demand books.
It’s free to publish your 1st ebook on PublishDrive. Or try out a paid plan and get your money back if you’re not satisfied.
How to Publish Your Print-on-Demand Book with PublishDrive
Here are a few easy steps to self-publish your print-on-demand book with PublishDrive.
Note: Currently, we do not offer a hardcover book option for print-on-demand books, only paperback. We are working on bringing this service to our users.
1. Format your manuscript
With print-on-demand books, there are two main PDF files to have ready:
- A file that includes the front cover, back cover, spine, and bleed area.
- The second file is your main manuscript which should follow these guidelines.
2. Log in / Create a PublishDrive account
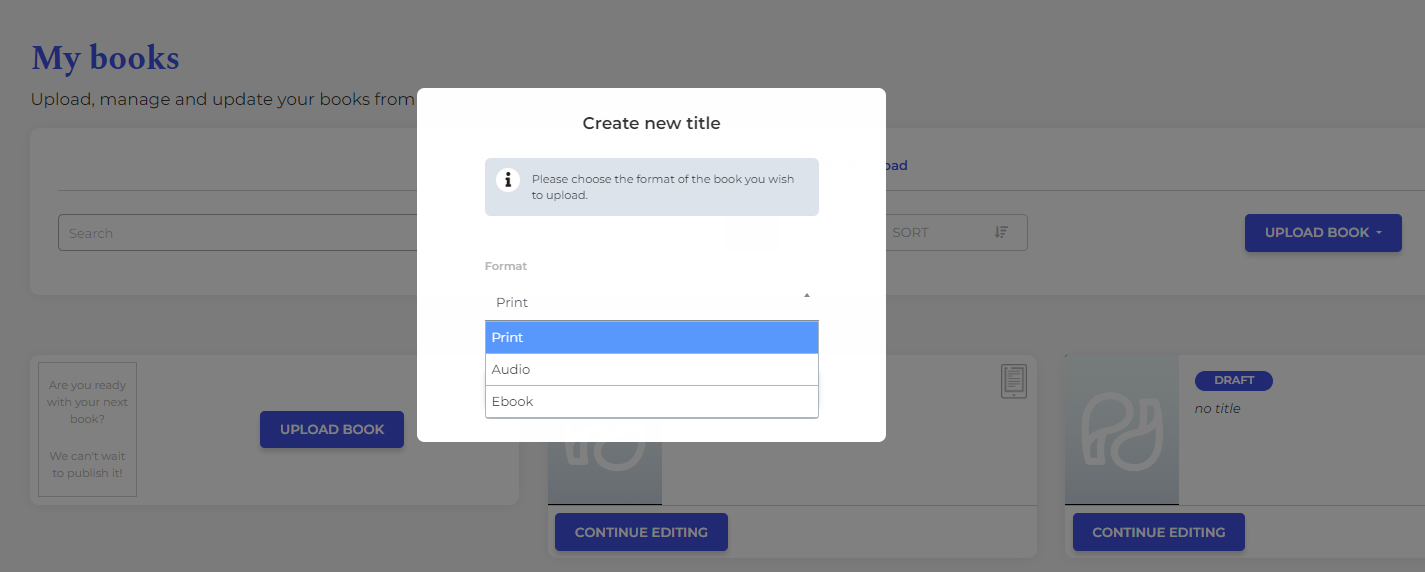
3. Upload your book
From the dashboard, go to My Books > Upload book and select the format.
4. Set up the manufacturing details
For print-on-demand books, you need to set up the manufacturing information: trim size, binding type, interior color, paper color, cover laminate type, and page count.
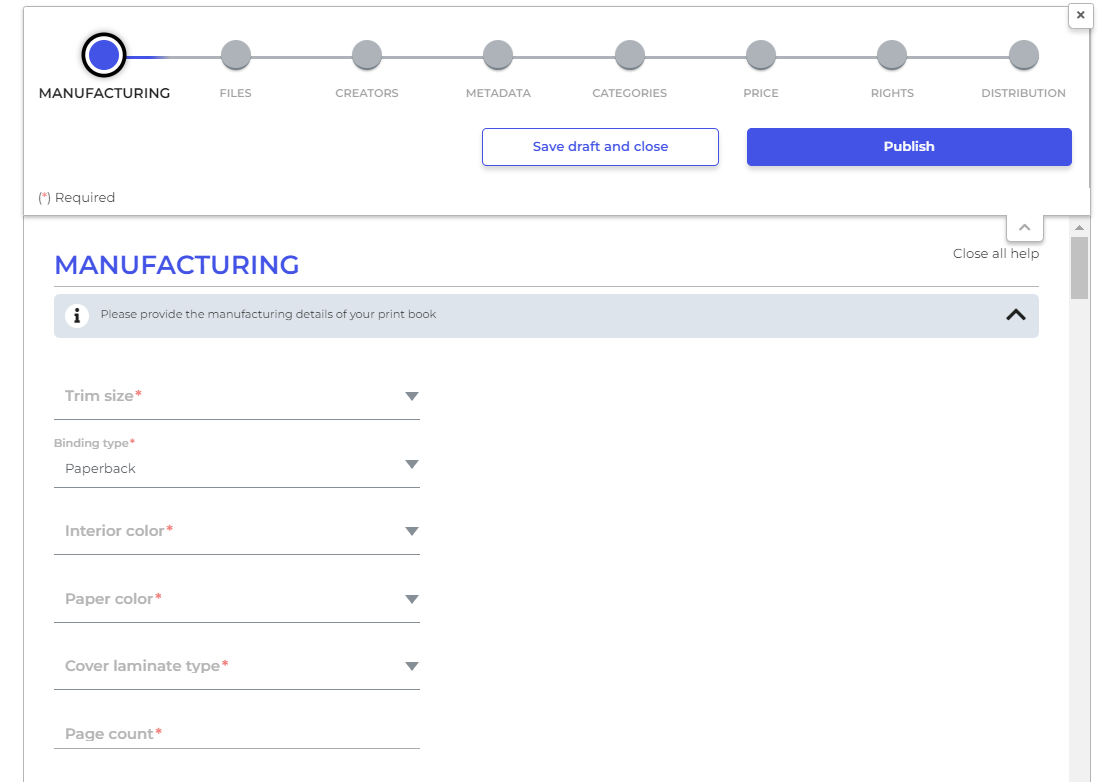
5. Upload your files
When uploading your files, make sure you adhere to the print-on-demand requirements. To simplify the process of creating your files, try PublishDrive’s print cover template generator, which you’ll find on the left-hand side of the main dashboard.
6. Fill out the book details
Add information on the book’s creators, metadata, categories, price, and rights (here, you can also set a pre-order for your book).
7. Select the distribution
PublishDrive collaborates with prominent distribution partners for print-on-demand services, including Amazon, Ingram, and China Print. Among these partners, Ingram Printing stands out as a leading company in the print-on-demand industry, serving a vast network of over 39,000 partners such as Barnes & Noble, Baker & Taylor, Target, and more.

Pitch Your Book to Local Bookstores
If you want to go beyond the distribution a print-on-demand service offers and display your book in local physical bookstores, you can do that, even if you’re a self-published author who chose print-on-demand technology.
Here’s how.
1. Get your book online
Before anything else, you need to publish and distribute your book online, but you should also enable the stores that allow print-on-demand.
2. Promote your book
A bookstore needs to know people are interested in a book before displaying it.
This means that you need to make a plan that creates demand for your book before pitching it to physical bookstores. Even if people go to bookstores to buy their next read, they still do their research online. That’s why you need to make your book available and visible online.
As a self-published author, you need a book marketing plan with a well-defined timeline that’ll guide you through every step of the book promotion.
3. Pitch your book to local bookstores
Once you’ve created interest around your book, contact a few local bookstores. Since this means you have to print copies of your book in advance, you should opt for risk-free methods such as:
- Requesting consignment sales: Contact bookstores and propose the option of selling your book on consignment. This arrangement allows the bookstores to sell your book and pay you a portion of the proceeds only when copies are actually sold.
- Prioritize local establishments: If the bookstores are unwilling to accept consignment sales, focus on local stores. In this scenario, the bookstores can return any unsold copies to you. Alternatively, if they decline consignment and opt to purchase your books, you will be required to reimburse them for their expenses.
4. Ask for author copies in PublishDrive
With our direct distribution feature (in beta version at the moment, but you can make a request to try it), you can order copies to be printed from your print-on-demand (POD) titles uploaded to PublishDrive. You can use these copies for commercial resells, signings, promotions, gifts, and more.
You can order print copies of a particular title from one (or both) of the available distribution stores when the title is shown as Available in the My books section in your account.
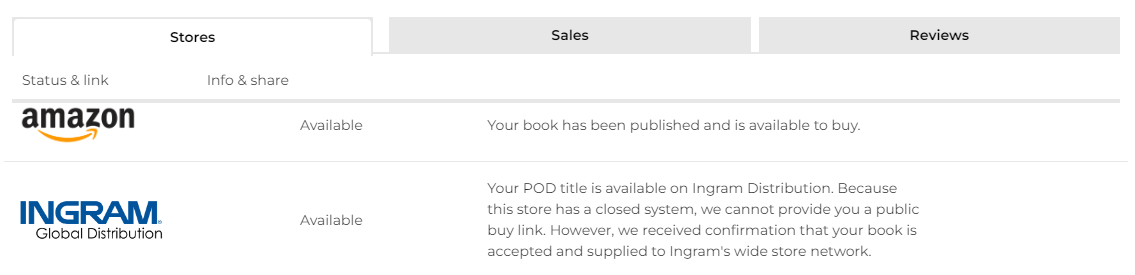
All features related to print copies can be found in your PublishDrive dashboard Print copy order.
For a detailed how-to process on this feature, check out our support article.
Wrapping Up
As a self-published author, it’s good to know how to price print-on-demand books to make a profit out of your sold books, of course.
Also, you can control the print production cost of your physical books by opting for print-on-demand that works with digital printing: it saves time, money, and it’s better for the environment because there’s never going to be any waste. At the same time, your readers will always have the option to buy your book.